1.日期与时间
1.1.概述
日期是指某一天,它不是连续变化的,例如:2019-11-11
而时间有两种概念,一种是不带日期的时间,例如,12:30:59。另一种是带日期的时间,例如,2020-1-1 20:21:59,只有这种带日期的时间才能能唯一确定的某个时刻,不带日期的时间是无法确定一个唯一时刻的。
因为全球不同地方的时区是不同的,相对的某个时区的时间是不同的,所以现在要确定某一个时刻也就需要通过日期+时间+时区共同组合才能完成并确定某一个时刻。
1.2.1本地时间
本地时间,是指每个地方根据其相对于太阳的位置而确定的本地时间,本地时间也指我们所处的当地时间,例如,中国北京时间,中国北京时间就是日期时间和中国时区组合(日期时间+本地时区)才是本地时间,所处地方不同本地时间也就不同,因为时区不同。
1.3.2.时区
时区有好几种表示方式。
第一种:GMT或者UTC加时区偏移表示时区
GMT或者UTC加时区偏移表示时区,例如:GMT+08:00或者UTC+08:00表示东八区,GMT和UTC可以认为基本是等价的,只是UTC使用更精确的原子钟计时,每隔几年会有一个闰秒,我们在开发程序的时候可以忽略两者的误差,因为计算机的时钟在联网的时候会自动与时间服务器同步时间。
第二种:缩写表示时区
缩写表示时区缩写,例如,CST表示China Standard Time,也就是中国标准时间。但是CST也可以表示美国中部时间Central Standard Time USA,因此,缩写容易产生混淆,我们尽量不要使用缩写。
第三种:以洲/城市表示时区
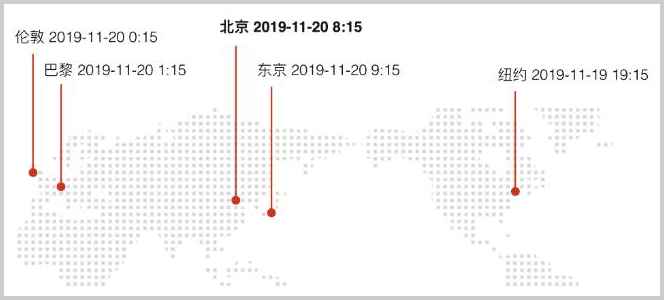
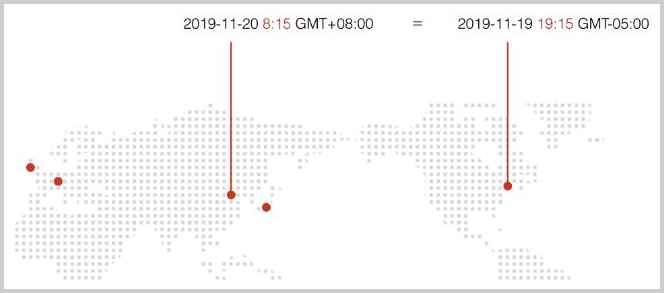
以洲/城市表示时区,例如,Asia/Shanghai,表示上海所在地的时区。特别注意城市名称不是任意的城市,而是由国际标准组织规定的城市,因为时区的存在,东八区的2019年11月20日早上8:15,和西五区的2019年11月19日晚上19:15,他们的时刻是相同的,但是因为洲/城市表示各个国家的可能
1.4.3.夏令时
所谓夏令时,就是夏天开始的时候,把时间往后拨1小时,夏天结束的时候,再把时间往前拨1小时。我们国家实行过一段时间夏令时,1992年就废除了,但是矫情的美国人到现在还在使用,所以时间换算更加复杂
因为夏令时的存在,虽然说时区相同,但是时间却是不同的。
对于2019-11-20和2019-6-20两个日期来说,假设北京人在纽约
如果以
GMT或者UTC作为时区,无论日期是多少,时间都是19:00;如果以国家/城市表示,例如
America/NewYork,虽然纽约也在西五区,但是,因为夏令时的存在,在不同的日期,GMT时间和纽约时间可能是不一样的,
注意:实行夏令时的不同地区,进入和退出夏令时的时间很可能是不同的,计算夏令时,没有统一的公式,必须按照一组给定的规则来算,并且,该规则要定期更新,因此计算夏令时请使用标准库提供的相关类,不要试图自己计算夏令时。
1.5.4.本地化
在计算机中,通常使用Locale表示一个国家或地区的日期、时间、数字、货币等格式。
Locale由语言_国家的字母缩写构成,例如,zh_CN表示中文+中国,en_US表示英文+美国。语言使用小写,国家使用大写。
对于日期来说,不同的Locale表示的格式是不同的,例如,中国和美国的表示方式如下:
zh_CN:2016-11-30
en_US:11/30/2016
计算机用Locale在日期、时间、货币和字符串之间进行转换。一个电商网站会根据用户所在的Locale对用户显示如下:
1.2.Date对象
1.2.1.概述
java.util.Date是用于表示一个日期和时间的对象,他实际上存储的是一个长整型数据表示的时间戳(Epoch Time)。
时间戳(Epoch Time)可以表示某一时刻,通过它和时区进行组合就得到了我们需要的日期时间
时间戳(Epoch Time)是计算从1970年1月1日零点(格林威治时区/GMT+00:00)到现在所经历的秒数,全球各个地方的时间戳是一样的,例如:
1574208900表示从1970年1月1日零点GMT时区到该时刻一共经历了1574208900秒,换算成伦敦、北京和纽约时间分别是:
1574208900 = 北京时间2019-11-20 8:15:00
= 伦敦时间2019-11-20 0:15:00
= 纽约时间2019-11-19 19:15:00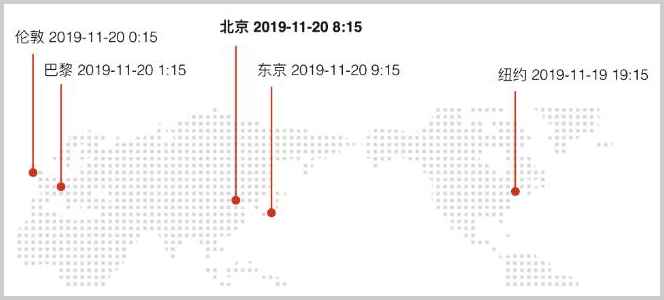
通过查看源码可以看到这个fastTime字段就是存储的时间戳
public class Date implements Serializable, Cloneable, Comparable<Date> {
private transient long fastTime; //存储时间戳
public long getTime() { //返回时间戳
return getTimeImpl();
}
...
}1.2.2.Date的基本使用
import java.util.Date;
public class MyDatetime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前时间:
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date.getTime()); // 返回毫秒时间戳
System.out.println(date.getYear() + 1900); // 必须加上1900
System.out.println(date.getMonth() + 1); // 0~11,必须加上1
System.out.println(date.getDate()); // 1~31,不能加1
// 转换为String:
System.out.println(date.toString());
// 转换为GMT时区:
System.out.println(date.toGMTString());
// 转换为本地时区:
System.out.println(date.toLocaleString());
// 时间戳转换为Date对象
Date date1=new Date(date.getTime())
System.out.println(date1.toLocaleString());
}
}结果:
1744538175948
2025
4
13
Sun Apr 13 17:56:15 CST 2025
13 Apr 2025 09:56:15 GMT
2025-4-13 17:56:151.2.3.SimpleDateFormat格式化输出与输入
通过结果可以看到将其转换字符串的形式显示,会有不同的结果,所以为了统一可以使用专门的格式日期类进行格式化输出。
SimpleDateFormat用于格式化和以区分区域设置的方式解析日期。它允许格式化(日期→文本)、解析(文本→日期)和规范化
SimpleDateFormat对一个Date进行转换,用预定义的字符串表示格式化:
yyyy:年
MM:月
dd: 日
HH: 小时
mm: 分钟
ss: 秒
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class MyDate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前时间:
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println("-----SimpleDateFormat格式化Date输出----------");
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat =
new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒");
String format = simpleDateFormat.format(date);
System.out.println(format);
System.out.println("------通过格式字符串和日期文本解析成Date对象------");
Date parseToDate = simpleDateFormat.parse("2020年04月13日 18时07分27秒", new ParsePosition(0));
System.out.println(parseToDate);
}
}1.2.4.Date日期对象的不足
Date对象有几个严重的问题:它不能转换时区,除了toGMTString()可以按GMT+0:00输出外,Date总是以当前计算机系统的默认时区为基础进行输出。此外,我们也很难对日期和时间进行加减,计算两个日期相差多少天,计算某个月第一个星期一的日期等。
1.3.Calendar对象
java.util.Calendar可以用于获取并设置年、月、日、时、分、秒,Calendar和Date相比比,多了可以做简单的日期和时间运算的功能,多了可以设置时区的功能,缺点是没有专门的Calendar格式化输出。
1.3.1.TimeZone时区
Calendar对象通过设置TimeZone时区对象就可以设置时区
时区的唯一标识是以字符串表示的ID,我们获取指定TimeZone对象也是以这个ID为参数获取,GMT+09:00、Asia/Shanghai都是有效的时区ID。要列出系统支持的所有ID,请使用TimeZone.getAvailableIDs()。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TimeZone tzDefault = TimeZone.getDefault(); // 当前时区
TimeZone tzGMT9 = TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT+09:00"); // GMT+9:00时区
TimeZone tzNY = TimeZone.getTimeZone("America/New_York"); // 纽约时区
System.out.println(tzDefault.getID()); // Asia/Shanghai
System.out.println(tzGMT9.getID()); // GMT+09:00
System.out.println(tzNY.getID()); // America/New_York
String[] availableIDs = TimeZone.getAvailableIDs();//获取全部时区id
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(availableIDs));
}
}1.3.2.Calendar的基本使用
Calendar对象不能直接格式化,需要先将Calendar对象转换为Date对象再用SimpleDateFormat进行格式化输出
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class MyCalendar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前时间,默认当地时区
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
int y = c.get(Calendar.YEAR); //年
int m = c.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1; //月份0-11 月份需要加一
int d = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH); //一个月中的第几天
int w = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK); //1~7分别表示 周日,周一,……,周六。
int hh = c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY); //小时
int mm = c.get(Calendar.MINUTE);//分钟
int ss = c.get(Calendar.SECOND); //秒
int ms = c.get(Calendar.MILLISECOND);//毫秒
System.out.println("本地时间:"+y + "-" + m + "-" + d + " " + w + " " + hh + ":" + mm + ":" + ss + "." + ms);
//转换为Date,再格式化输出
Date date = c.getTime();
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒").format(date));
}
}设置Calendar的时区
注意:因为Date没有时区,它本质就是存储的时间戳,当使用Calendar实例的getTime()方法转换为Date对象时,设置的时区就不起作用了
解决办法是通过SimpleDateFormat继承过来的setTimeZone方法设置时区,让日期对象以特定时区格式化
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class MyCalendar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 设置时区,获取美国纽约时区时间
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(TimeZone.getTimeZone("America/New_York"));
int y = c.get(Calendar.YEAR); //年
int m = c.get(Calendar.MONTH)+1; //月份0-11 月份需要加一
int d = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH); //一个月中的第几天
int w = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK); //1~7分别表示 周日,周一,……,周六。
int hh = c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY); //小时
int mm = c.get(Calendar.MINUTE);//分钟
int ss = c.get(Calendar.SECOND); //秒
int ms = c.get(Calendar.MILLISECOND);//毫秒
System.out.println("美国纽约时间:"+y + "-" + m + "-" + d + " " + w + " " + hh + ":" + mm + ":" + ss + "." + ms);
//转换为Date,设置的美国纽约时区失效
Date date = usCalendar.getTime();
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒");
//设置美国纽约时区
simpleDateFormat.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("America/New_York"));
System.out.println("美国纽约时间:"+simpleDateFormat.format(date));
}
}1.3.3.Calender日期运算
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 当前时间:
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
// 清除所有:
c.clear();
// 设置年月日时分秒:
c.set(2019, 10 /* 11月 */, 20, 8, 15, 0);
// 加5天并减去2小时:
c.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 5);
c.add(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, -2);
// 显示时间:
var sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date d = c.getTime();
System.out.println(sdf.format(d));
// 2019-11-25 6:15:00
}
}1.4.LocalDateTime对象
1.4.1.概述
从Java 8开始,java.time包提供了新的日期和时间API,主要涉及的类型有:
本地日期和时间:
LocalDateTime,LocalDate,LocalTime;带时区的日期和时间:
ZonedDateTime;时刻:
Instant;时区:
ZoneId,ZoneOffset;时间间隔:
Duration格式化输出:
DateTimeFormatter
DateTimeFormatter格式化输出
新的格式化类型DateTimeFormatter用于取代旧的SimpleDateFormat。因为SimpleDateFormat不是线程安全的,使用的时候,只能在方法内部创建新的局部变量,而DateTimeFormatter可以只创建一个实例,到处引用
新的时间API修正了旧API不合理的常量设计:
Month的范围用1~12表示1月到12月;
Week的范围用1~7表示周一到周日。
1.4.2.LocalDateTime基本使用
LocalDateTime、LocalDate和LocalTime默认严格按照ISO 8601规定的日期和时间格式进行打印。ISO 8601规定的日期和时间分隔符是T
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
public class MyLocalDateTime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate d = LocalDate.now(); // 根据默认系统时区当前日期
LocalTime t = LocalTime.now(); // 当前时间
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.now(); // 当前日期和时间
System.out.println(d); // 严格按照ISO 8601格式打印
System.out.println(t); // 严格按照ISO 8601格式打印
System.out.println(dt); // 严格按照ISO 8601格式打印
//LocalDateTime转LocalDate,通过该方式可以避免获取时间不一致问题
LocalDate localDate = dt.toLocalDate();
//LocalDateTime转LocalTime
LocalTime localTime = dt.toLocalTime();
//将ISO 8601的格式日期字符串转换为LocalDataTime
LocalDateTime parse = LocalDateTime.parse("2019-11-19T15:16:17");
System.out.println(parse);
//获取美国时区的时间,
LocalDateTime nowUS = LocalDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("America/New_York"));
System.out.println("美国时间:"+nowUS);
}
}输出结果
2025-04-13
22:32:00.410
2025-04-13T22:32:00.410
2019-11-19T15:16:171.4.3.DateTimeFormatter格式化输出与输入
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class MyLocalDateTime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将ISO 8601的格式日期字符串转换为LocalDataTime
LocalDateTime parse = LocalDateTime.parse("2019-11-19T15:16:17");
System.out.println(parse);
//DateTimeFormatter格式化输出LocalDateTime
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒");
System.out.println(dateTimeFormatter.format(parse));//DateTimeFormatter的format方法格式化输出
System.out.println(parse.format(dateTimeFormatter));//LocalDateTime的format格式化输出
//使用时间字符串和格式字符解析生成LocalDateTime
//DateTimeFormatter的parse方法转换
LocalDateTime parse1 =
dateTimeFormatter.parse("2019年11月19日 15时16分17秒",LocalDateTime::from);
LocalDateTime parse1_1 =
dateTimeFormatter.parse("2019年11月19日 15时16分17秒",(temporal)->LocalDateTime.from(temporal));
LocalDateTime parse1_2 =
dateTimeFormatter.parse("2019年11月19日 15时16分17秒",new TemporalQuery<LocalDateTime>(){
public LocalDateTime queryFrom(TemporalAccessor temporal) {
return LocalDateTime.from(temporal);
}
});
//LocalDateTime的parse方法转换
LocalDateTime parse2 = LocalDateTime.parse("2019年11月19日 15时16分17秒",dateTimeFormatter);
System.out.println(parse1+" "+parse1_1+" "+parse1_2+" "+parse2);
}
}1.4.4.LocalDateTime日期时间运算
对LocalDateTime日期时间进行运算主要用到以下几个方法
增加plus系列:plusYear()、plusMonths()、plusDay()等。。。
减少minus系列:minusYear()、minusMonths()、minusDay()等。。
调整with系列:withYear()、withMonth()、withDayOfMonth()、withHour()、withMinute()、withSecond()等。。
复杂运行:with()
public class MyLocalDateTime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//对日期和时间进行加减操作
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.of(2019, 10, 26, 20, 30, 59);
System.out.println(dt);
// 加5天减3小时:
LocalDateTime dt2 = dt.plusDays(5).minusHours(3);
System.out.println(dt2); // 2019-10-31T17:30:59
// 减1月:
LocalDateTime dt3 = dt2.minusMonths(1);
System.out.println(dt3); // 2019-09-30T17:30:59
//对日期和时间进行调整使用withXxx()方法
/*调整年:withYear()
调整月:withMonth()
调整日:withDayOfMonth()
调整时:withHour()
调整分:withMinute()
调整秒:withSecond()*/
LocalDateTime dt4 = LocalDateTime.of(2019, 10, 26, 20, 30, 59);
System.out.println(dt);
// 日期变为31日:
LocalDateTime dt5 = dt.withDayOfMonth(31);
System.out.println(dt2); // 2019-10-31T20:30:59
// 月份变为9:
LocalDateTime dt6 = dt2.withMonth(9);
System.out.println(dt3); // 2019-09-30T20:30:59
//通用的with()方法允许我们做更复杂的运算
// 本月第一天0:00时刻:
LocalDateTime firstDay = LocalDate.now().withDayOfMonth(1).atStartOfDay();
System.out.println(firstDay);
// 本月最后1天:
LocalDate lastDay = LocalDate.now().with(TemporalAdjusters.lastDayOfMonth());
System.out.println(lastDay);
// 下月第1天:
LocalDate nextMonthFirstDay = LocalDate.now().with(TemporalAdjusters.firstDayOfNextMonth());
System.out.println(nextMonthFirstDay);
// 本月第1个周一:
LocalDate firstWeekday = LocalDate.now().with(TemporalAdjusters.firstInMonth(DayOfWeek.MONDAY));
System.out.println(firstWeekday);
//判断两个LocalDateTime的先后
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime target = LocalDateTime.of(2019, 11, 19, 8, 15, 0);
System.out.println(now.isBefore(target));
System.out.println(LocalDate.now().isBefore(LocalDate.of(2019, 11, 19)));
System.out.println(LocalTime.now().isAfter(LocalTime.parse("08:15:00")));
}
}1.4.5.Duration和Period时间间隔
Duration表示两个时刻之间的时间间隔
Period表示两个日期之间的天数
Duration和Period他们都是按照ISO 8601规定的日期和时间格式进行打印,它以P...T...的形式表示,P...T之间表示日期间隔,T后面表示时间间隔。如果是PT...的格式表示仅有时间间隔。
public class MyLocalDateTime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime start = LocalDateTime.of(2019, 11, 19, 8, 15, 0);
LocalDateTime end = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 1, 9, 19, 25, 30);
//Duration时间间隔
Duration d = Duration.between(start, end);
System.out.println(d); // PT1235H10M30S
//Period日期之间的天数
Period p = LocalDate.of(2019, 11, 19).until(LocalDate.of(2020, 1, 9));
System.out.println(p); // P1M21D
}
}1.4.6.LocalDateTime对象的缺点
LocalDateTime无法与时间戳进行转换,因为LocalDateTime没有自带时区(不存储时区),无法确定某一时刻,进行时间戳转换
1.5.ZonedDateTime时区日期时间
ZonedDateTime是自带时区的日期时间对象,可以实习时区转换,日期时间运算,使用时间戳转换
1.5.1.ZonedDateTime的基本使用
ZonedDateTime=LocalDateTime+ZoneId,LocalDateTime=ZonedDateTime+系统默认时区
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class MyZonedDateTime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZonedDateTime zbj = ZonedDateTime.now(); // 默认系统时区
ZonedDateTime zbj_1 = ZonedDateTime.of(LocalDateTime.now(), ZoneId.systemDefault());
ZonedDateTime zny = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("America/New_York")); // 用指定时区获取当前时间
System.out.println(zbj_1);
System.out.println(zbj);
System.out.println(zny);
//转换不同时区
ZonedDateTime timeCN = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
//上海时间转换为纽约时间:
ZonedDateTime timeUS = zbj.withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId.of("America/New_York"));
System.out.println(timeCN);
System.out.println(timeCN.toLocalDateTime());
System.out.println(timeUS.toLocalDateTime());
//转换为系统默认时区LocalDateTime,ZonedDateTime+默认系统时区=LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime localDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now().toLocalDateTime();
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = ZonedDateTime.now(Clock.systemDefaultZone()).toLocalDateTime();
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toLocalDateTime();
LocalDateTime localDateTime3 = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai")).toLocalDateTime();
System.out.println("默认系统时区:"+localDateTime+" "+localDateTime1+" "+localDateTime2+" "+localDateTime3 );
}
}1.5.2.DateTimeFormatter格式化输出与输入
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
public class MyZonedDateTime {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//格式化输出
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒");
String format = zonedDateTime.format(dateTimeFormatter);
System.out.println(format);
dateTimeFormatter.withZone(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
//格式化输入,注意格式化输入时需要指定时区,因为ZonedDateTime是自带有时区的
DateTimeFormatter formatter =
DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒").withZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
ZonedDateTime parse = ZonedDateTime.parse("2025年04月13日 12时18分11秒", formatter);
System.out.println(parse);
}
}1.6.Instant瞬时(时间戳)
计算机存储的当前时间,本质上只是一个不断递增的整数,System.currentTimeMillis()返回的就是以毫秒表示的当前时间戳,这个时间戳可以使用java.time.Instant对象存储。
1.6.1.Instant的基本使用
ZonedDateTime=时间戳(Instant)+时区(ZoneId)
import java.time.Instant;
public class MyInstant {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取当前时间戳
Instant instantNow = Instant.now();
long epochSecond = instantNow.getEpochSecond(); //秒时间戳
long epochMilli = instantNow.toEpochMilli();//毫秒时间戳
System.out.println(epochSecond);
System.out.println(epochMilli);
//Instant转换为ZonedDateTime,ZonedDateTime=时间戳(Instant)+时区(ZoneId)
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime
= Instant.now().atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
System.out.println(zonedDateTime)
}
}1.7.总结
Date和Calendar是java8之前的api,Date只能使用默认时区,可以进行时间戳转换,不能进行日期运算,Calendar可以设置时区,可以时间戳转换
LocalDateTime和ZoneDateTime是java8中新添加的api,LocalDateTime不存储时区,不可以时间戳转换,可以进行日期运算,ZoneDateTime可以设置时区,可以时间戳转换,可以进行时区转换,可以进行日期运算。
1.7.1.新老时间日期对象相互转换
本地日期时间(Date,Calendar、LocalDateTime、ZonedDateTime)=时间戳(Instant)+时区(TimeZone)
新老日期API的相互转换需要借助时间戳(Instant)来实现。
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.TimeZone;
public class EndMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//LocalDateTime----->Date
LocalDateTime localDateTimeNow = LocalDateTime.now();
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTimeNow = ZonedDateTime.of(localDateTimeNow, ZoneId.systemDefault());
Instant instant = zonedDateTimeNow.toInstant();
Date date = Date.from(instant);
System.out.println("LocalDateTimeNow:"+localDateTimeNow);
System.out.println("Date:"+date);
System.out.println("--------------");
//Date----->LocalDateTime
Date dateNow = new Date();
Instant instantDate = dateNow.toInstant();
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = instantDate.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
LocalDateTime localDateTime = zonedDateTime.toLocalDateTime();
System.out.println("Date:"+dateNow);
System.out.println("LocalDateTime:"+localDateTime);
System.out.println("***********************************");
//Calendar----->ZonedDateTime
Calendar calendarNow = Calendar.getInstance();
Instant instantNow = calendarNow.toInstant();
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime1
= ZonedDateTime.ofInstant(instantNow, ZoneId.systemDefault());
System.out.println(calendarNow);
System.out.println(zonedDateTime1);
System.out.println("--------------");
//ZonedDateTime----->Calendar
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now();
Instant instant1 = now.toInstant();
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.clear();
TimeZone timeZone = TimeZone.getTimeZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
calendar.setTimeZone(timeZone);
calendar.setTimeInMillis(instant1.toEpochMilli());
System.out.println(now);
System.out.println(calendar);
}
}1.7.2.数据库中的日期和java中的日期
在使用Java程序操作数据库时,我们需要把数据库类型与Java类型映射起来。下表是数据库类型与Java新旧API的映射关系:
实际上,在数据库中,我们需要存储的最常用的是时刻(Instant),因为有了时刻信息,就可以根据用户自己选择的时区,显示出正确的本地时间。所以,最好的方法是直接用长整数long表示,在数据库中存储为BIGINT类型,它具有省空间,效率高,不依赖数据库的优点。如果要用于时间筛选也可以通过将日期时间时间转换为时间戳然后在数据库中进行查询。
