1.手写MVC框架
MVC=ModelAndView(数据和视图)+Controller(由Servlet控制层实现)
Controller的方法定义的@Get或@Post的Path决定调用哪个方法,最后,获得方法返回的ModelAndView后,渲染模板,写入HttpServletResponse,即完成了整个MVC的处理。
这个MVC的架构如下:
HTTP Request ┌─────────────────┐
──────────────────▶│DispatcherServlet│
└─────────────────┘
│
┌────────────┼────────────┐
▼ ▼ ▼
┌───────────┐┌───────────┐┌───────────┐
│Controller1││Controller2││Controller3│
└───────────┘└───────────┘└───────────┘
│ │ │
└────────────┼────────────┘
▼
HTTP Response ┌────────────────────┐
◀────────────────│render(ModelAndView)│
└────────────────────┘
其中,DispatcherServlet以及如何渲染均由MVC框架实现,在MVC框架之上只需要编写每一个Controller,做到类似于下面这这种效果
@Controler
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/signin")
public ModelAndView signin() {
...
retrun new ModelAndView();
}
@PostMapping("/signin")
public ModelAndView doSignin(SignInBean bean) {
...
retrun new ModelAndView();
}
@GetMapping("/signout")
public ModelAndView signout(HttpSession session) {
...
retrun new ModelAndView();
}
}
1.1.实现思路
MVC=ModelAndView(数据和视图)+Controller(由Servlet控制层实现)
要实现MVC就需要让ModelAndView和Controller受MVC框管理和控制,如何让MVC管理和控制,可以通过以下步骤实现:
第一:接管所有请求,可以通过编写一个Sevlet类并设置为接收根请求(“/”),这里我创建的是一个名为ServletDispatcher的Servlet类,如下
@WebServlet("/")
public class ServletDispatcher extends HttpServlet {
//代码省略
}
第二:管理和控制ModelAndView,ModelAndView其实就是将HTML模板(View)和数据模型(View)进行关联和渲染,这些都可以使用第三方的模板引擎(Thymeleaf、FreeMarker、Velocity、pebbletemplates等)来做具体实现,我们要做的就是通告写一个视图引擎来调用第三方的模板引擎,我这里创建的是一个名为ViewEngine的类来调用第三方模板引擎,内容如下:
public class ViewEngine {
public ViewEngine(ServletContext servletContext) {
//创建第三方模板引擎,可以查看第三方模板引擎文档再编写
//创建第三方模板引擎代码省略。。。。
}
public void render(ModelAndView mv, Writer writer){
//将ModelAndView的Model数据和View视图路径交给第三方模板引擎去渲染,可以查看第三方模板引擎文档再编写
//然后生成字节字节码,赋值给Writer对象
//代码省略。。。。。
}
}
因为ModelAndView其实就是将HTML模板(View)和数据模型(View)进行关联和渲染,需要HTML模板所以我们必须存储一个返回HTML模板的路径,数据模型可以使用键值对的方式存储任意类型数据,让所以可以定义为以下内容:
public class ModelAndView {
private Map<String,Object> model;
private String view;
//省略其它代码。。。。
}
第三:管理和控制Controller,实际上处理网络请求的是Sevlet类,Controller类并不能直接接收到网络请求的,但是我们所有的网络请求路径都写在了Controller类的@GetMapping和@PostMapping中了,所有我们需要想办法的得到这些Controller类还有Controller类中的@GetMapping和@PostMapping中的请求路径以及@GetMapping和@PostMapping修饰的方法发的参数,再调用@GetMapping和@PostMapping修饰的方法,如何拿到以上说的信息呢?答案是反射,通过反射可以轻松拿到刚才说的所有信息。在Servlet类中通过反射来管理和控制Controller类,如何实现这个管理和控制Controller是MVC框架的重点,这些控制方法将会写在接管所有网络请求的ServletDispatcher中,其内容基本如下
@WebServlet("/")
public class ServletDispatcher extends HttpServlet {
//存储请求路径String和请求处理类Dispatcher的映射,请求处理类Dispatcher类中主要存储的是反射信息,
private final Map<String, Dispatcher> postRequestMappings=new HashMap<>();
private final Map<String, Dispatcher> getRequestMappings=new HashMap<>();
//所有的Controller类字节码
private final Set<Class<?>> allControllers=new HashSet<>();
//模板引擎,处理渲染HTML模板
private ViewEngine viewEngine;
//。。。。。。
@Override
public void init() {
//初始化步骤如下
//1.获取到所有的Controllerl类的字节码存储到allControllers类中,方便后续通过反射得到类中相关信息
//2.通过allControllers类中字节码,获取类中相关信息,将请求路径String和请求处理类Dispatcher进行映射存储到postRequestMappings和getRequestMappings映射表中
//3.初始化第三方模板引擎,方便后续直接调用渲染
}
}
1.2.代码实现
1.2.1.创建MVC的相关注解
以下是@Controller、@GetMapping、@PostMapping的创建,
后面可以通过字节码的isAnnotationPresent()方法判断是否类或者方法方法上是否添加了相关类型的注解,通过字节码的getAnnotation()可以获取到注解并拿到注解中的参数
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Controller {
}
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target(METHOD)
public @interface GetMapping {
String value();
}
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Target(METHOD)
public @interface PostMapping {
String value();
}
1.2.2.bean实体(测试)
用于测试Controller类的返回ModelAndView
public class SignInBean {
public String email;
public String password;
}
public class User {
public String email;
public String password;
public String name;
public String description;
public User() {
}
public User(String email, String password, String name, String description) {
this.email = email;
this.password = password;
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
}
}
1.2.3.创建ModelAndView
public class ModelAndView {
private Map<String,Object> model;
private String view;
public ModelAndView(String view) {
this.view = view;
}
public ModelAndView(String view,String key,Object object) {
HashMap<String, Object> stringObjectHashMap = new HashMap<>();
stringObjectHashMap.put(key,object);
this.model=stringObjectHashMap;
this.view=view;
}
public ModelAndView(String view,Map<String, Object> model) {
this.model = model;
this.view = view;
}
public Map<String, Object> getModel() {
return model;
}
public String getView() {
return view;
}
}
1.2.1.创建相关Controller类
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/")
public ModelAndView index(HttpSession session) {
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
return new ModelAndView("/index.html", "user", user);
}
@GetMapping("/hello")
public ModelAndView hello(String name) {
if (name == null) {
name = "World";
}
return new ModelAndView("/hello.html", "name", name);
}
}
@Controller
public class UserController {
private Map<String, User> userDatabase = new HashMap<>() {
{
List<User> users = List.of( //
new User("bob@example.com", "bob123", "Bob", "This is bob."), new User("tom@example.com", "tomcat", "Tom", "This is tom."));
users.forEach(user -> {
put(user.email, user);
});
}
};
@GetMapping("/signin")
public ModelAndView signin() {
return new ModelAndView("/signin.html");
}
@PostMapping("/signin")
public ModelAndView doSignin(SignInBean bean, HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session) throws IOException {
User user = userDatabase.get(bean.email);
if (user == null || !user.password.equals(bean.password)) {
response.setContentType("application/json");
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
pw.write("{\"error\":\"Bad email or password\"}");
pw.flush();
} else {
session.setAttribute("user", user);
response.setContentType("application/json");
PrintWriter pw = response.getWriter();
pw.write("{\"result\":true}");
pw.flush();
}
return null;
}
@GetMapping("/signout")
public ModelAndView signout(HttpSession session) {
session.removeAttribute("user");
return new ModelAndView("redirect:/");
}
@GetMapping("/user/profile")
public ModelAndView profile(HttpSession session) {
User user = (User) session.getAttribute("user");
if (user == null) {
return new ModelAndView("/signin");
}
return new ModelAndView("/profile.html", "user", user);
}
}
1.2.5.创建ViewEngine类
该类是用于调用第三方模板引擎将HTML视图模板和Model数据模型进行渲染,具体如何创建第三方模板引擎和如何通过第三方模板引擎渲染视图和数据可以参看第三方模板引擎的官方文档,我这里使用的thymeleaf模板引擎,其他模板引擎(FreeMarker、Velocity、pebbletemplates等)理论来说也一样。
public class ViewEngine {
private final TemplateEngine TemplateEngine ;
private final ServletContext servletContext;
//通过构造方法创建thymeleaf模板引擎
public ViewEngine(ServletContext servletContext) {
this.servletContext=servletContext;
JavaxServletWebApplication application = JavaxServletWebApplication.buildApplication(servletContext);
// Templates will be resolved as application (ServletContext) resources
final WebApplicationTemplateResolver templateResolver =
new WebApplicationTemplateResolver(application);
// HTML is the default mode, but we will set it anyway for better understanding of code
templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.HTML);
// html模板存放的位置
templateResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/templates/");
templateResolver.setSuffix(".html");
// Set template cache TTL to 1 hour. If not set, entries would live in cache until expelled by LRU
templateResolver.setCacheTTLMs(Long.valueOf(3600000L));
// Cache is set to true by default. Set to false if you want templates to
// be automatically updated when modified.
templateResolver.setCacheable(false);
// 设置解析后生成的模板编码,不然中文乱码
templateResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
final TemplateEngine templateEngine = new TemplateEngine();
templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(templateResolver);
this.TemplateEngine= templateEngine;
}
//通过thymeleaf模板引擎对HTML视图模板和Model数据模型进行渲染
public void render(ModelAndView mv, Writer writer) throws IOException {
TemplateSpec templateSpec = new TemplateSpec(mv.getView(), (String) null);
Context context = new Context(Locale.CHINA);
context.setVariables(mv.getModel());
this.TemplateEngine.process(templateSpec,context,writer);
}
}
1.2.6.创建相关Dispatcher请求处理类
Dispatcher接口
所有请求处理类都将实现该接口
public interface Dispatcher {
ModelAndView invoke(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception;
}
Post网络请求处理类
因为post请求一般用于json的传输,所以psot请求处理方法,参数只有HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse、HttpSession、Bean实体类 这4种类型,其中Bean实体类需要需要通过将传输过来的json数据转换为Bean实体类,这里用的是jackson工具将json转换为Bean实体类。
public class PostDispatcher implements Dispatcher {
private Object instance; //存储通过反射创建的Controller类实例,后面通过反射调用方法会用
private Method method; //存储通过反射获取Controller类的带@PostMapping注解的请求方法,后面会通过属性调用
final ObjectMapper objectMapper; //该属性是jackson的对象映射,它会post提交的json映射为实体bean
private Class<?>[] parameterTypes; //psot网络请求方法中参数的类型
public PostDispatcher(Object instance, Method method, ObjectMapper objectMapper, Class<?>[] parameterTypes) {
this.instance = instance;
this.method = method;
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
}
public Object getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public Method getMethod() {
return method;
}
public ObjectMapper getParameterNames() {
return objectMapper;
}
public Class<?>[] getParameterTypes() {
return parameterTypes;
}
@Override
public ModelAndView invoke(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
//存储所有参数的对象实例,后面method.invoke调用方法会用到
Object[] arguments = new Object[parameterTypes.length];
//遍历带@PostMapping注解的方法参数的类型,将匹配的类型存储到arguments数组中
for (int i = 0; i < parameterTypes.length; i++) {
Class<?> parameterClass = parameterTypes[i];
if (parameterClass == HttpServletRequest.class) { //方法参数有HttpServletRequest类型
arguments[i] = request; //将HttpServletRequest对象存储到arguments数组中
} else if (parameterClass == HttpServletResponse.class) {
arguments[i] = response;
} else if (parameterClass == HttpSession.class) {
arguments[i] = request.getSession();
} else {
BufferedReader reader = request.getReader(); //获取post请求携带的json数据
arguments[i] = this.objectMapper.readValue(reader, parameterClass);//使用jackson的对象映射方法将json数据映射为对应的Bean实体类
}
}
return (ModelAndView) this.method.invoke(instance, arguments); //通过反射调用对应的psot网络处理方法
}
}
get网络请求处理类
因为get请求一般用于基本数据类型的传输,他通过浏览器的地址栏输入参数然后传输,所以get请求处理方法,参数除了HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse、HttpSession、这3种类型外,还包含其他例如 int、String、long、boolean、double基本类型。
public class GetDispatcher implements Dispatcher {
private Object instance;//存储通过反射创建的Controller类实例,后面通过反射调用方法会用
private Method method;//存储通过反射获取Controller类的带@GetMapping注解的请求方法,后面会通过属性调用
private String[] parameterNames; //get网络请求处理方法中参数的名字
private Class<?>[] parameterTypes; //get网络请求处理方法中参数的类型
public GetDispatcher(Object instance, Method method, String[] parameterNames, Class<?>[] parameterTypes) {
this.instance = instance;
this.method = method;
this.parameterNames = parameterNames;
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
}
public Object getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public Method getMethod() {
return method;
}
public String[] getParameterNames() {
return parameterNames;
}
public Class<?>[] getParameterTypes() {
return parameterTypes;
}
@Override
public ModelAndView invoke(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
int length = parameterNames.length;
//存储所有参数的对象实例,后面method.invoke调用方法会用到
Object[] arguments = new Object[length];
for (int i=0;i<length;i++){
String parameterName = parameterNames[i];
Class<?> parameterClass = parameterTypes[i];
if (parameterClass == HttpServletRequest.class) { //方法参数有HttpServletRequest类型
arguments[i] = request //将HttpServletRequest对象存储到arguments数组中
} else if (parameterClass == HttpServletResponse.class) {
arguments[i] = response;
} else if (parameterClass == HttpSession.class) {
arguments[i] = request.getSession();
} else if (parameterClass == int.class) { //方法参数有int基本类型
//将int基本类型的包装类对象存储到arguments数组中
arguments[i] = Integer.valueOf(getOrDefault(request, parameterName, "0"));
} else if (parameterClass == long.class) {
arguments[i] = Long.valueOf(getOrDefault(request, parameterName, "0"));
} else if (parameterClass == boolean.class) {
arguments[i] = Boolean.valueOf(getOrDefault(request, parameterName, "false"));
} else if (parameterClass == double.class) {
arguments[i] = Double.valueOf(getOrDefault(request, parameterName, "false"));
} else if (parameterClass == String.class) {
arguments[i] = getOrDefault(request, parameterName, "");
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Missing handler for type: " + parameterClass);
}
}
//通过反射调用对应的get网络处理方法
return (ModelAndView) this.method.invoke(this.instance, arguments);
}
//如果传入的基本类型没有赋值时设定一个默认值
private String getOrDefault(HttpServletRequest request, String name, String defaultValue) {
String s = request.getParameter(name);
return s == null ? defaultValue : s;
}
}
1.2.7.创建FileServlet静态资源处理
该类用于返回/static路径下的静态资源例如图片、js文件、css文件等
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = { "/favicon.ico", "/static/*" })
public class FileServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext ctx = req.getServletContext();
// RequestURI包含ContextPath,需要去掉:
String urlPath = req.getRequestURI().substring(ctx.getContextPath().length());
// 获取真实文件路径:
String filepath = ctx.getRealPath(urlPath);
if (filepath == null) {
// 无法获取到路径:
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
Path path = Paths.get(filepath);
if (!path.toFile().isFile()) {
// 文件不存在:
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
// 根据文件名猜测Content-Type:
String mime = Files.probeContentType(path);
if (mime == null) {
mime = "application/octet-stream";
}
resp.setContentType(mime);
// 读取文件并写入Response:
OutputStream output = resp.getOutputStream();
try (InputStream input = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(filepath))) {
input.transferTo(output);
}
output.flush();
}
}
1.2.8.创建MVC核心处理类ServletDispatcher
ServletDispatcher类通过反射来管理和控制Controller类,是整个MVC框架的重点,特别是初始化方法的实现。
@WebServlet("/") //接管所有的网络请求,是个sevlet类,因为只有sevlet类可以接收到网络请求
public class ServletDispatcher extends HttpServlet {
//存储请求路径String和请求处理类Dispatcher的映射,请求处理类Dispatcher类中主要存储的是反射信息,
private final Map<String, Dispatcher> postRequestMappings=new HashMap<>();
private final Map<String, Dispatcher> getRequestMappings=new HashMap<>();
//所有的Controller类字节码
private final Set<Class<?>> allControllers=new HashSet<>();
//模板引擎,处理渲染HTML模板
private ViewEngine viewEngine;
@Override
public void init() { //初始化方法,当该类被调用创建时会调用一次,后面不在调用
System.out.println("初始化");
try {
//1)获取所有的Controller字节码(包扫描),存储到allControllers中
scannerPackage();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
//2)将请求路径url和Dispatcher请求处理类实例键值映射并存入Map
handleRequestMappings();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//3)初始化视图引擎,传入ServletContext上下文,sevlet类可以直接获取到
this.viewEngine=new ViewEngine(getServletContext());
}
//1)获取所有的Controller字节码(包扫描),存储到allControllers中
public void scannerPackage() throws Exception{
String packagePath="com.web.mvc.controller";
scannerPackage(packagePath);
}
public void scannerPackage(String packagePath) throws Exception {
String filePath=packagePath.replace(".", File.separatorChar+"");
URL resourcePath = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource(filePath);
if (resourcePath==null){
throw new IOException("包路径未找到:"+packagePath);
}
File file = new File(resourcePath.getFile()+"");
//得到com.web.mvc.controller包中的所有文件(类和文件夹)
File[] files = file.listFiles();
assert files != null;
//遍历所有的文件,并得到controller类的字节码,存储到allControllers中
listFiles(files,packagePath);
}
private void listFiles(File[] files,String packagePath) throws Exception {
for (File item : files){
if (item.isFile()&&item.getName().endsWith(".class")){
String tempPath=packagePath+"."+
item.getName().replace(".class","");
//到controller类的字节码并存储到allControllers中
this.allControllers.add(Class.forName(tempPath));
}else if (!item.isFile()){
listFiles(Objects.requireNonNull(item.listFiles()),packagePath+"."+item.getName());
}
}
}
//2)将请求路径url和Dispatcher请求处理类实例键值映射并存入Map
private void handleRequestMappings() throws Exception {
//遍历所有的controller字节码
for (Class<?> item:this.allControllers){
//检查该controller字节码类上是否添加上了@Controller注解
if (!item.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class)){
continue;
}
//通过controller类的字节码用反射实例化controller对象
Object controllerItem = item.getConstructor().newInstance();
//controller类的字节码得到所有controller类中的方法
Method[] methods = item.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) { //遍历controller类中的方法
//判断controller类中的方法是否添加@GetMapping注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(GetMapping.class)){
GetMapping annotation = method.getAnnotation(GetMapping.class); //得到@GetMapping注解
String value = annotation.value(); //得到@GetMapping注解的参数,也就是网络请求路径
//通过stream流将get网络请求处理方法中的所有参数名称转换为String类型的数组
String[] parameterNames
= Arrays.stream(method.getParameters()).map(temp -> temp.getName()).toArray(String[]::new);
//创建get网络请求处理类对象实例,
//controllerItem是反射创建的controller实例,
//method是controller实例中的get网络请求处理方法
//parameterNames是get网络请求处理方法中的所有参数名
//method.getParameterTypes()是get网络请求处理方法中的所有参数的类型
GetDispatcher getDispatcher
= new GetDispatcher(controllerItem, method, parameterNames, method.getParameterTypes());
//将get网络请求路径url和GetDispatcher网络请求处理类实例键值映射并存入getRequestMappings
getRequestMappings.put(value,getDispatcher);
//判断controller类中的方法是否添加@GetMapping注解
}else if (method.isAnnotationPresent(PostMapping.class)){
PostMapping annotation = method.getAnnotation(PostMapping.class);//得到@PostMapping注解
String value = annotation.value();//得到@PostMapping注解中的参数值
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); //jackson工具中的类对象用于将Json数据转为Bean实体
//创建psot网络请求处理类对象实例,
//controllerItem是反射创建的controller实例,
//method是controller实例中的psot网络请求处理方法
//objectMapper是jackson工具中的类对象用于将Json数据转为Bean实体
//method.getParameterTypes()是post网络请求处理方法中的所有参数的类型
PostDispatcher postDispatcher
= new PostDispatcher(controllerItem, method, objectMapper, method.getParameterTypes());
//将psot网络请求路径url和PostDispatcher网络请求处理类实例键值映射并存入postRequestMappings
postRequestMappings.put(value,postDispatcher);
}
}
}
}
//MVC核心方法,该方法用于控制和调用controller类
private void process(HttpServletRequest req,
HttpServletResponse resp,
Map<String, ? extends Dispatcher> requestMappings) throws Exception {
//得到网络请求中的请求路径
String requestURI = req.getRequestURI();
//通过网络请求路径得到网络请求处理类(GetDispatcher或者PostDispatcher)对象
Dispatcher dispatcher = requestMappings.get(requestURI);
if (dispatcher == null) {
resp.sendError(404);
return;
}
ModelAndView mv = null;
//调用网络请求处理类(GetDispatcher或者PostDispatcher)对象中controller实例的post或者get网络请求处理方法得到ModelAndView,这里比较绕,可以多看下
ModelAndView invoke = dispatcher.invoke(req, resp);
if (invoke==null){ //处理psot网络请求处理方法中返回的null值
return;
}
mv=invoke;
//通过HttpServletResponse对象设置响应http的header信息
resp.setContentType("text/html");
resp.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
//通过HttpServletResponse对象设置响应http的body信息
PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter();//获取字节码
this.viewEngine.render(mv, pw);//调用模板引擎渲染html页面,并作为http的body响应体
//刷新缓存,将http信息响应给浏览器
pw.flush();
}
//sevlet类中继承的方法,所有的get请求将调用
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
try {
//调用MVC核心方法,该方法用于控制和调用controller类,注意这里传入的是getRequestMappings
process(req,resp,this.getRequestMappings);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//sevlet类中继承的方法,所有的post请求将调用
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
try {
//调用MVC核心方法,该方法用于控制和调用controller类,注意这里传入的是postRequestMappings
process(req,resp,this.postRequestMappings);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
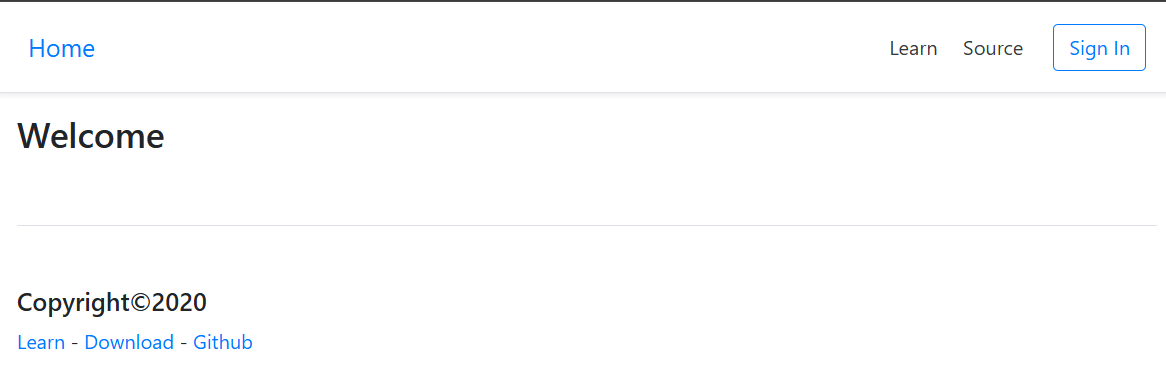
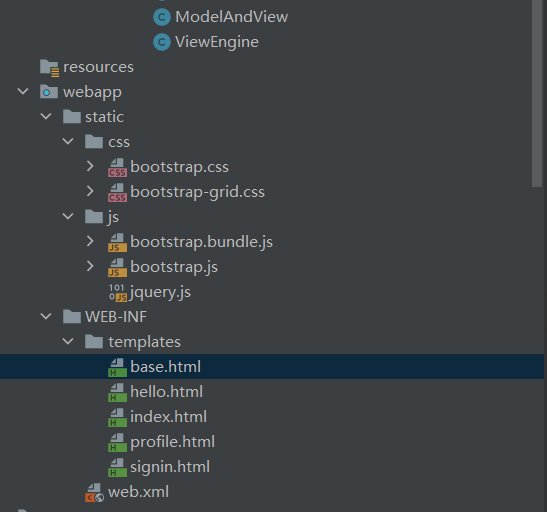
1.2.9.创建html模板
我这里用的thymeleaf模板引擎,具体语法可以查看thymeleaf官方文档
base.html
<!doctype html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" th:fragment="html (head,content)">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<title>MVC</title>
<script src="/static/js/jquery.js"></script>
<link href="/static/css/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body style="font-size:16px" >
<div class="d-flex flex-column flex-md-row align-items-center p-3 px-md-4 mb-3 bg-white border-bottom shadow-sm">
<h5 class="my-0 mr-md-auto font-weight-normal"><a href="/">Home</a></h5>
<nav class="my-2 mr-md-3">
<a class="p-2 text-dark" target="_blank" href="https://www.leduo.com/">Learn</a>
<a class="p-2 text-dark" target="_blank" href="#">Source</a>
</nav>
<th:block th:if="${user==null}">
<a href="/signin" class="btn btn-outline-primary">Sign In</a>
</th:block>
<th:block th:if="${user!=null}">
<span>Welcome, <a href="/user/profile">[[${user.name}]]</a></span>
<a href="/signout" class="btn btn-outline-primary">Sign Out</a>
</th:block>
</div>
<div class="container" style="max-width: 960px">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-12 col-md">
<section>
<th:block th:replace="${content}"/>
</section>
</div>
</div>
<footer class="pt-4 my-md-5 pt-md-5 border-top">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-12 col-md">
<h5>Copyright©2020</h5>
<p>
<a target="_blank" href="https://www.leduo.work/">Learn</a> -
<a target="_blank" href="https://www.leduo.work/">Download</a> -
<a target="_blank" href="https://www.leduo.work/">Github</a>
</p>
</div>
</div>
</footer>
</div>
</body>
</html>
hello.html
<div th:replace="~{base :: html(head = null,content = ~{::content})}">
<th:block>
<h3>hello [[${name}]]!</h3>
</th:block>
</div>
index.html
<div th:replace="~{base :: html(head = null,content = ~{::content})}">
<th:block th:fragment="content">
<th:block th:if="${user!=null}">
<h3>Welcome [[${user.name}]]!</h3>
</th:block>
<th:block th:if="${user==null}">
<h3>Welcome</h3>
</th:block>
</th:block>
</div>
profile.html
<!doctype html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" th:replace="~{base::html (head=null,content=~{::Profile})}">
<th:block th:fragment="Profile">
<h3>Profile</h3>
<p>Email: [[${ user.email }]]</p>
<p>Name: [[${user.name}]]</p>
<p>Description: [[${user.description}]]</p>
</th:block>
</html>
signin.html
<th:block th:replace="~{base::html (head=null,content=~{::#signinForm})}">
<div>
<form id="signinForm">
<div class="form-group">
<p id="error" class="text-danger"></p>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Email</label>
<input id="email" type="email" class="form-control" placeholder="Email">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Password</label>
<input id="password" type="password" class="form-control" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-outline-primary">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
</th:block>
<script>
console.log("sasasasaassa")
$(function () {
console.log("sasasasaassa")
$('#signinForm').submit(function (e) {
e.preventDefault();
var data = {
email: $('#email').val(),
password: $('#password').val()
};
$.ajax({
type: 'POST',
url: '/signin',
data: JSON.stringify(data),
success: function (resp) {
if (resp.error) {
$('#error').text(resp.error);
} else {
location.assign('/');
}
},
contentType: 'application/json',
dataType: 'json'
});
});
});
</script>
1.2.10.pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/1.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-1.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>1.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.web.mvc</groupId>
<artifactId>webmvc</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>web-mvc</name>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.10.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>3.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!--war打包插件-->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
1.2.11.总结
管理和控制Controller是MVC的核心,而MVC的核心的核心是通过反射获取Controller类实现控制和调用。
github源码地址:https://github.com/AllenWarg/servlet-mvc
gieet源码地址:https://gitee.com/cgh-yfx/servlet-mvc
运行结果如下: